Acid Reflux Got You Down?
In addition to the flavor, aroma, and health benefits that a cup of coffee can offer, there are other factors to consider when selecting a beans for brewing. One of these is the acidity of coffee.
Acidity is an important aspect of coffee because it affects the overall taste and determines whether or not a cup of coffee might be considered a light or dark roast. Acidity can also impact the amount of caffeine present in a cup, with some roasts having more than others.
Additionally, several compounds are released during the roasting process which contribute to flavor and aroma such as lipids and carbohydrates. Understanding these components can help you to customize your coffee experience for maximum enjoyment.
If you love coffee but suffer from acid reflux, you’ve likely asked yourself whether coffee is alkaline.
The short answer is… it depends. Different brewing methods, additives, and brands all play a role in making coffee more alkaline or acidic. Read on to learn how to make your cup of java less acidic and more palatable.
So What is Alkaline Coffee? Alkaline coffee is made with a different brewing process than regular coffee. It’s generally brewed using cold water and has been aged in an oxygen-free environment for up to seven days. This aging process reduces the acidity of the brew, making it easier on your stomach.
When selecting an alkaline coffee, it’s important to consider the type of beans used.
The most popular variety is a light roasted arabica bean, but other types such as dark-roasted robusta and medium-roasted blends can also be found in alkaline coffees. Additionally, some brands add baking soda during the brewing process to further reduce the acidity.
Preparing alkaline coffee is similar to regular cold brew coffee, but the ratio of grounds to water may be slightly different. Since it’s a cold-brew process, start with equal parts cold water and ground coffee. Let it steep for about 12 hours in the refrigerator before straining out the grounds. Cold brew coffee is my go-to during the warmer summer months. Do not use instant arabica coffee powder for this. Instant coffee powders are usually not alkaline in nature and can give you trouble.
Related Article: 5+ Amazing Benefits of Drinking Date Seed Coffee

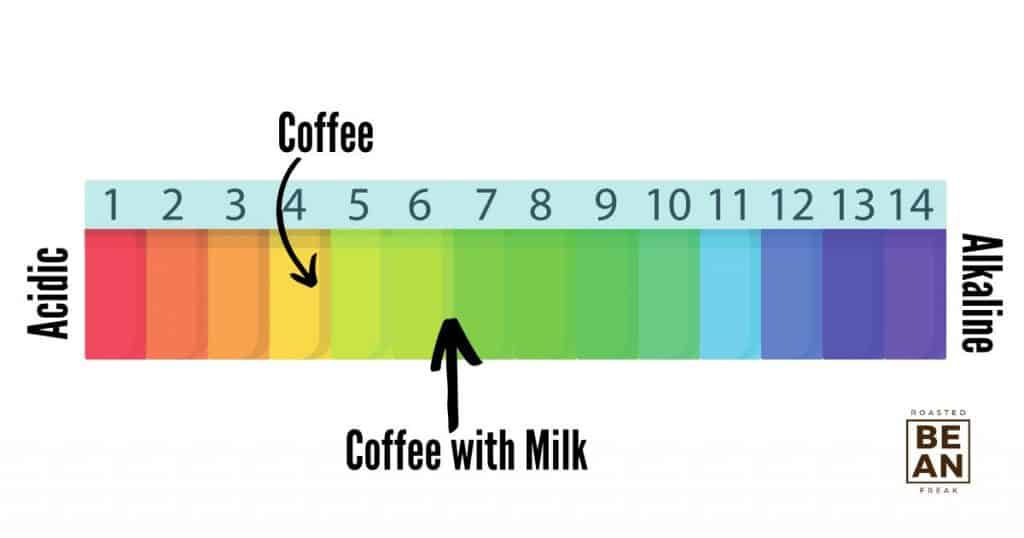
Is Coffee Alkaline?
The pH level of plain brewed coffee averages between 4.85 and 5.10, which makes it slightly acidic. However, ordering a latte or cappuccino with milk can raise the pH level to 6 or 7, which is closer to neutral.
So if you need an alkaline option for your daily cup of joe, consider adding some milk or cream instead of drinking black coffee.
The pH scale is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a substance is. It ranges from 0 to 14, where anything below 7 is considered acidic, while anything above 7 is alkaline. Coffee generally has an acidic pH level due to its high levels of caffeine and other natural compounds.
Additionally, the acidity levels will vary depending on the brew method used so it’s important to consider that as well when choosing how you want to prepare your coffee.
How To Make Coffee Less Acidic
There are several ways you can make your coffee less acidic. First, try using cold-brewed coffee instead of hot-brewed. Cold-brewing reduces the acidity by making the coffee smooth and not bitter.
You can also opt for a light roast coffee, as dark roasts have higher acidity. Finally, try adding some milk or cream for a more neutral flavor that is less acidic and more palatable.
Related Article: Does Cinnamon Reduce Acid in Coffee?
Is Decaf Coffee Low Acid?
Decaf coffee does contain lower levels of acidity than regular coffee, but it still contains some acidic compounds. Depending on how the beans are decaffeinated, some processes can reduce the levels even further.
So overall, decaf coffee may be a better option for those looking for an acidic drink that won’t cause heartburn or upset stomach. However, it’s important to remember that unless the coffee is 100% decaf, it will still contain some acidity.
Milk vs Almond Milk vs Oat Milk
The best alkaline coffee creamer is any type of dairy or non-dairy creamer to be honest. Milk is the most common way to reduce acidity in coffee. Adding a splash of milk can raise the pH level to 6 or 7, which is closer to neutral. The added fat and proteins also provide an additional layer of flavor and creaminess.
Almond milk adds a nutty quality to the coffee, while also making it less acidic. It’s low in fat and high in calcium and is a great option for those looking to reduce their dairy intake.
Oat milk also adds a nutty sweetness to the coffee, but with a creamy texture and even lower acidity than almond milk. The added oats provide a subtle flavor and added texture, which can really enhance the overall taste of the coffee. Oat milk is also high in protein and fiber content.
No matter which type you choose to reduce acidity in your coffee, it’s important to remember that these are all dairy alternatives and may not be suitable for everyone. Make sure to check the ingredients label to ensure that it meets your dietary needs.
Related Article: Coffee Revolution: How Oat Milk Is Transforming Your Daily Brew
Brewing A Less Acidic Coffee
To further reduce the acidity levels in your regular cup of Joe, try adding some baking soda or lemon juice before brewing your coffee. Adding either one will help neutralize the acids present in the grounds while still allowing you to enjoy a delicious cup of coffee without any added sugar or creamers.
You can also try using cold brew instead of hot-brewed coffee as this method has been found to produce less acidic beverages due to its longer brewing time and colder temperature.
Additionally, adding some greens such as kale or spinach to your morning routine can help balance out the acidic effects of caffeine intake by providing much-needed vitamins and minerals!
Does Cinnamon Reduce Acid in Coffee
Adding cinnamon to your coffee may surprise you, but it can help lower its acid levels. Cinnamon is a natural way to reduce the acidity of coffee without altering its flavor. It’s a simple and easy way to make coffee more enjoyable for those with sensitive stomachs.
You can add the cinnamon to either the coffee grounds before you brew your coffee, or sprinkle a bit on top of the finished cup. Whichever way you choose, adding cinnamon to your coffee is an easy way to reduce acidity and bring out its flavors.
Low Acid Coffee Brands
If you’re looking for a low acid coffee brand that will soothe your stomach rather than aggravate it, look no further than Lifeboost Coffee – 100% Organic Premium Arabica Beans Medium Roast Low Acid Ground (or Lifeboost Coffee Pods).
Lifeboost is one of the only alkaline coffee brands to only use certified organic beans grown in the mountains of Nicaragua and processes them slowly at low temperatures to reduce acidity without sacrificing flavor. There are a few others and I have links to those below.
For those who like a stronger brew, Lifeboost also offers two darker roasts – Dark Roast and Espresso – both of which are lower in acidity than most other brands on the market.
|
$33.38 ($0.17 / Fl Oz)
|
N/A
|
15,95 €
|
|
Acids Found in Coffee
Coffee is one of the most popular drinks around the world, but it can also be quite acidic. Acidity levels in coffee vary based on factors such as brewing method, bean type, and roast level.
Different types of acids found in coffee include chlorogenic acid (CGA), quinic acid, citric acid, malic acid, acetic acid and phosphoric acid. These acids all play a role in creating the flavor profile of your cup of joe – from its bitterness to its sweetness – while also having an effect on how acidic or alkaline your drink is overall.
Knowing more about these different types of acids can help you understand how they contribute to your favorite brews!
Acetic Acid vs Organic Acids
When it comes to understanding different types of acids in relation to coffee consumption, there are two main categories – acetic acid and organic acids (such as chlorogenic acids).
Acetic acid is typically present in higher concentrations in dark roast coffees whereas organic acids tend to be higher in medium roast coffees due to their shorter roasting times and cooler temperatures used during processing.
Quinic Acid
Quinic acid is an important organic acid found in coffee. It is responsible for adding a mild sourness to the cup, and it can also help to modulate bitterness when balanced with other acids present in the beverage.
While quinic acid levels can vary from bean to bean, its presence generally increases when dark roasted beans are used for brewing. Additionally, its concentration increases as the brewing temperature rises.
Therefore, for those looking to reduce quinic acid levels in their cup of coffee, light roasts and lower temperatures are recommended.
Chlorogenic Acids
Chlorogenic acids (CGAs) are naturally occurring compounds found in the majority of coffee beans. CGAs have been linked to several health benefits and are largely responsible for the antioxidant profile in coffee.
There is a large difference in CGA levels between coffees, with darker roasts having lower concentrations of these acids than lighter roasts. Additionally, some brewing methods can extract more chlorogenic acids from the beans as compared to others.
It’s beneficial to consider both roast and brewing method when trying to increase chlorogenic acid content in coffee.
Chlorogenic acid
Chlorogenic acid is a natural organic compound found in coffee beans and has been linked to various health benefits, including improved cognitive function, weight loss, and lower blood pressure.
Caffeine, on the other hand, is a stimulant that may improve alertness and focus but can also cause jitters or insomnia if consumed in excess. Different roasting methods affect the amount of chlorogenic acid and caffeine within a coffee bean, so it’s important to keep the temperature in mind when you roast.
For example, higher temperatures can reduce the amount of both compounds while lower temperatures will preserve them more (though they might not be as pronounced).
Ultimately, depending on your desired outcome, you should experiment with different roasting techniques to find the best flavor and health benefits.
Caffeine Content of Coffee
Caffeine is the most popular bioactive compound found in coffee and is largely responsible for its psychoactive effects. The caffeine concentration of a cup of coffee depends on both the roast level and brewing method used, but it can vary greatly between different types of coffee beans.
Generally, lighter roasted beans have higher caffeine content than dark roasted ones. Additionally, some brewing methods (e.g. espresso) can extract more caffeine from the beans compared to other methods (e.g. French press).
Therefore, it’s important to consider both roast and brewing method when trying to increase or decrease the caffeine content in coffee.
Related Article: Arabica vs. Robusta Showdown: Which Bean Will Reign Supreme?
Wrapping this up… coffee beans are rich in beneficial compounds like chlorogenic acid and caffeine. Depending on your desired outcome, different roasting techniques can be used to impact the amount of these compounds within a particular bean.
By experimenting with different temperatures and methods, you can find the flavor and health benefits that best suit you. With this knowledge, you can now enjoy the perfect cup of coffee.
Looking for more coffee questions and answers for your next jeopardy appearance? Check out our FAQ page for more!






